Is RPA Losing Its Edge?
Nearly every industry is feeling the pressure from economic uncertainty and a tight labor market. It’s during these times that organizations look to increase efficiencies and cut costs, targeting inefficient manual processes that hamper agility and prevent the delivery of a differentiating product or service.
But economic headwinds don’t need to be a source of uncertainty. In fact, Gartner argues that a recession presents an opportunity for businesses to build a long-term competitive advantage by investing in the right digital initiatives.1
In an effort to maintain a competitive edge, many businesses have turned to RPA. Unfortunately, these companies have also discovered that the solution they opted for is far more rigid than they first believed—as soon as a process changes, the automation breaks, requiring constant testing and rebuilding of bots.
What most business leaders don’t realize is that only 20% of their available data can be processed by RPA. Without including processes that handle unstructured data (something RPA struggles with) in the automation pipeline, automation efforts screech to a halt.
This ebook will help you better understand the limitations of traditional RPA solutions, as well as offer insight about how intelligent automation adds significant value to an existing RPA setup. With a more accurate and flexible automation solution in place, businesses can optimize operations while better supporting the needs of customers.
Businesses are Outgrowing RPA
Historically, RPA has been the enterprise’s automation tool of choice for one simple reason—RPA solutions perform rules-based tasks quickly and accurately. However, as digital transformation initiatives mature, businesses are shifting their focus from automating singular, simple tasks to the automation of entire complex, end-to-end processes.
If digital transformation is akin to running a marathon, RPA will only take you the first few miles. While it works for simple, well-defined tasks, it lacks the intelligence and flexibility required to automate increasingly complex processes—and it won’t get you to the finish line. According to a September 2022 report from HFS Research2
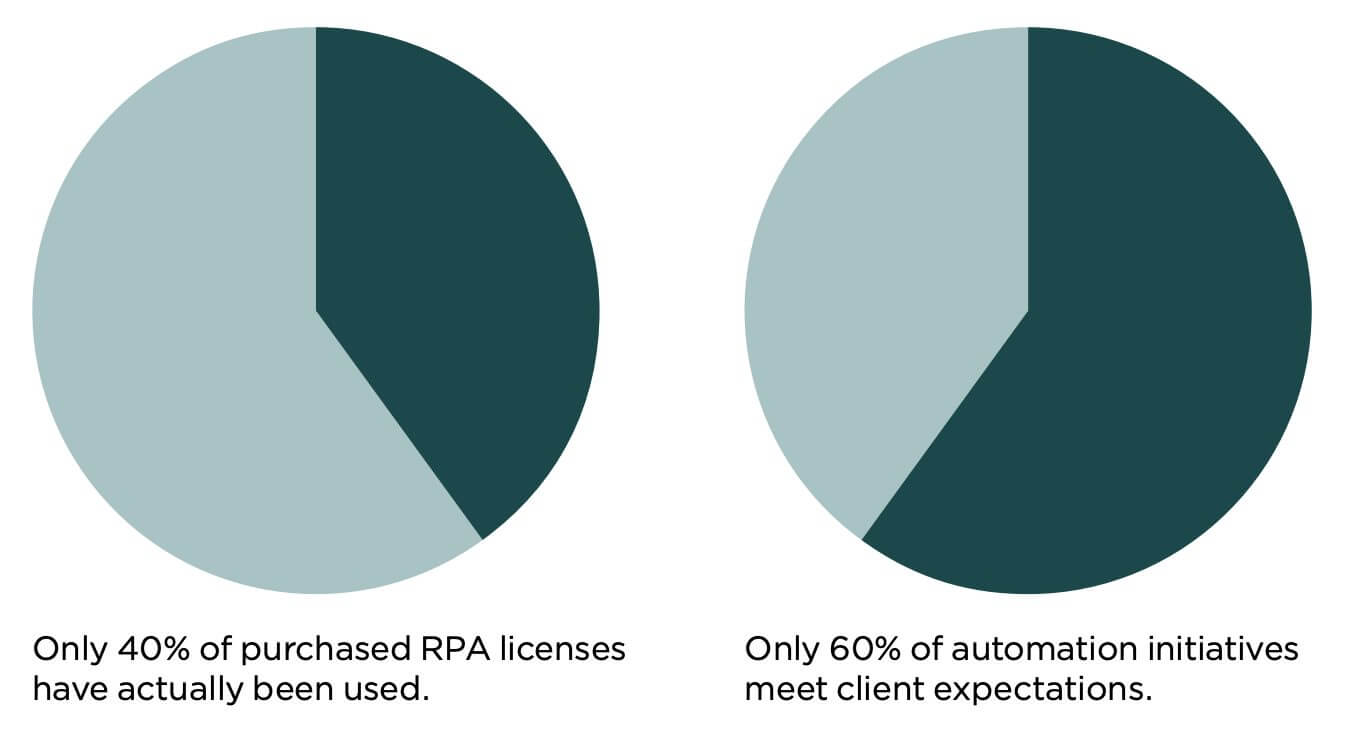
With an RPA solution in place, it can actually be more challenging to sunset legacy software or even perform basic updates. As processes change, software robots (called digital workers by many RPA vendors) break—and create costly mess in doing so. Regarding this, the HFS Research study estimates the shelf life of an RPA Bot to be between 9-18 months. After that timeframe, system and process changes either necessitate a rework or make it redundant.
The Macro Problem: Mountains of Unstructured Data
Unstructured data includes information acquired via emails and text-heavy documents and PDFs, along with rich media formats like images, video, and voice/audio. According to estimates from Gartner, unstructured data accounts for as much as 80% of an enterprise’s total data.3
RPA relies on rigid business rules and a template-based approach that can’t handle the unpredictability and high variability of most unstructured formats. An unstructured document, like a contract or a medical record, with long paragraphs of text, doesn’t have predefined or predictable fields to extract information from.
What this means for companies deploying RPA-centric automation is that 80% of their data remains trapped in documents and other content types that their automation solution can’t read.
RPA’s failure to automate processes reliant on unstructured data impedes an organization’s economic resilience and operational agility in several ways:
Increased Costs
Organizations that rely heavily on manual processes to handle unstructured data may see a significant increase in costs due to the need for manual labor. This can be particularly challenging for organizations that operate in highly competitive or fast-moving markets, where keeping costs low is critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
Inefficient Processes
RPA is not designed to handle unstructured data and as a result, manual processes are required to process this type of data which can lead to inefficiency. This can slow down operations and reduce the overall agility of an organization, making it more difficult to respond quickly to changing conditions or customer needs.
Restricted Insights
Unstructured data can contain valuable insights that organizations can use to improve their operations and make better-informed decisions. However, if RPA cannot process this data, organizations may miss out on these insights, which can limit their ability to innovate and adapt.
Limited Scalability
As an organization grows and the volume of unstructured data increases, manual processes can become overwhelming, limiting the scalability of the organization.
RPA’s inability to automate processes involving unstructured data can have a significant impact on an organization’s ability to operate efficiently, respond to changing market conditions, and extract valuable insights from data.
For companies seeking resilience and agility, this unstructured data must be unlocked.
Where RPA Falls Short
When RPA was first introduced, it offered a quick and simple way to automate some of the repetitive back office business processes without the need of APIs. As a result, RPA came to be viewed as the easiest point of entry for many digital transformation initiatives. However, as organizations began implementing RPA solutions and those implementations matured, companies began seeing first-hand the constraints of RPA. Some of those limitations include:
Struggling with Complex Processes
Business processes are often quite complex with multiple steps, conditions, and decisions to be made before arriving at a final outcome. RPA bots may struggle with such complexity, and as a result, they may not be able to automate the entire process.
For example, business processes frequently change, such as when a software application or even an entire system receives an upgrade. For complex processes with many moving parts, even the slightest change can cause an RPA bot to break.
Reliance on Templates
For RPA to work with document-centric processes (which are the vast majority), it requires a new template to be created for each document variance.
Before RPA bots can accurately automate invoice processing, a template must be created for each invoice format received, which can easily be in the hundreds or thousands for large organizations. Highly variable documents are harder to standardize, resulting in high maintenance costs and process exceptions that must be handled manually.
Requiring Additional Technology
Where RPA fails, additional automation tools such as intelligent document processing (IDP) or optical character recognition (OCR) are needed to translate the unstructured information into structured data that—once a template has been created—can be processed by RPA.
While many RPA vendors already offer these capabilities through 3rdparty providers, it’s not proprietary technology, which adds complexity and more costs to existing automation initiatives.
Poor Scalability
RPA struggles to scale as it relies on predefined rules and templates to automate tasks. As the number of processes and tasks increase, it becomes more challenging to manage and maintain the bots, and there is a risk of the rules and templates becoming out of date or inconsistent. When a process becomes more complex and exceptions arise, it can become harder for the RPA to handle it and the process needs to be reevaluated.
Failure to Recognize and Learn From Mistakes
Since not all possible exceptions can be programmed into its logic, a software bot will simply stop or, even worse, carry on unaware of the mistake it made. If unchecked, this leads to real-world ramifications, such as an individual not receiving their disability benefit or a delayed insurance claim.
Going Beyond RPA with Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation represents a shift in automation where machines imitate human actions and possess cognitive abilities, typically through the use of machine learning. Intelligent automation solutions can comprehend structured and unstructured data, as well as learn from ingested data, making it possible for businesses to automate processes more fully.
Intelligent document processing (IDP) is a powerful example of intelligent automation in action, helping organizations increase efficiency and accuracy when dealing with huge volumes of data.
“Organizations looking for ways to apply AI pragmatically today should prioritize investigating intelligent document processing.”4 Neil Ward-Dutton, Vice President of AI, Automation, and Analytics, IDC Europe
IDP technologies add value by increasing agility, as well as automation scope and rate, and helps process documents with greater speed and accuracy than traditional automation technology.
Intelligent Automation Vs. RPA
Intelligent automation helps organizations build automated processes that are flexible and work in tandem with business objectives. Where RPA is more rigid and would break down or throw an exception when the process changes, intelligent automation has the ability to continuously learn and adapt to changes in the business. Intelligent automation accomplishes increasingly complex tasks with better accuracy, greater connectivity, and endless flexibility.
Benefits of Intelligent Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) and its related technologies are creating a sea of change, altering the way businesses simplify and expedite complex workflows. Processes like mortgage loan originations, benefits claims, and social services programs are prime candidates for smarter automation practices.
Companies desiring greater flexibility and resilience have begun the shift from RPA alone to intelligent automation solutions, where machine learning (ML) and AI work alongside humans for faster and more accurate data processing, end-to-end automation, and increased operational scalability.
Here are some of the advantages of intelligent automation solutions.
Equipped for Unstructured Data
By leveraging AI and ML, this form of automation is able to turn human-made content into machine-readable data. ML enables the automated processing of low resolution images, scanned documents, PDFs—all the unstructured data mentioned previously—even with messy handwritten text, crossed out information, or other data degradations.
Increased Accuracy and Efficiency
Intelligent automation handles increasingly complex processes with greater accuracy and reliability. Instead of a single bot repeatedly performing the same task with no variation, imagine a solution that automates dynamic, data-centric workflows while being smart enough to know when to ask for human interaction to achieve better outcomes and make better decisions.
Improved Customer Experience
Intelligent automation has the potential to greatly improve the customer experience by providing more personalized and efficient service, increasing availability, and proactively addressing customer needs. It can also help organizations make more informed decisions by providing them with more accurate and consistent customer data.
Better Employee Engagement
Intelligent automation has the potential to improve employee engagement by reducing repetitive tasks, encouraging skills development, and by improving process efficiency. As a result, employees can spend more time on more meaningful work, which can lead to higher satisfaction, motivation and better job performance.
More End-to-End Automation
Intelligent automation can provide more end-to-end automation of processes for businesses by automating repetitive tasks, identifying and prioritizing tasks, predictive maintenance, process optimization, and integration with other systems. This can help organizations improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make better-informed decisions without relying on multiple disparate tools.
Customer Story: Intelligent Automation in Action
At CI Financial, when an agent managed a case, they manually read, processed, and transcribed any documents related to that case. Manual processing strained the company’s operations and challenged its ability to scale.
Integrating Intelligent Automation with RPA
While CI’s existing RPA solution streamlined some rules-based tasks for the company, it ultimately lacked the ability to read unstructured document data, which proved to be a roadblock in unlocking greater automation initiatives. By bolstering their RPA solution with Hyperscience, CI Financial could unlock the data previously trapped in unstructured documents.
Automation, Fully Realized
CI Financial uses a combination of RPA and intelligent automation to automate document-driven processes. Hyperscience helps reduce the time it takes agents to type case documents by 60%, giving them more time to focus on other activities that contribute to providing the best customer experience.
“We experienced a 142% increase in the number of documents routed to the automation, and we’ve seen a 253% increase in documents processed through the automation queue.” Martin Cheung Vice President of Digital Transformation & Automation CI Financial
Augmenting RPA with Intelligent Automation
For those relying solely on RPA to carry the load of today’s complex business processes—the limitations of rules-based technology can’t keep up with modern business. Companies that complement their existing automation stack with ML technology that continuously learns from data and improves over time, increase the speed and quality of their operations and business outcomes while cutting costs, mitigating risks, and boosting revenue.
Watch this short platform demo to see how Hyperscience leverages proprietary Machine Learning to extract data from complex documents.
1 Gartner: Recession Advice: Go on the Offensive with IT Investments GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and is used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
2 HFS: Automation is Back with a Bang
3 Gartner: Organizations Will Need to Tackle Three Challenges to Curb Unstructured Data Glut and Neglect GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and is used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
