Understanding the Landscape
Since 1967, the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) has provided the public with the right to request access to records from any federal agency. The agency must then disclose any information requested—unless it falls under 1 of 9 exemptions that protect interests such as personal privacy, national security, and law enforcement. Similarly, the Privacy Act of 1974 provides individuals the right to request their personal records from any federal agency, subject to exemptions.
And while the U.S. Government’s push for records transparency nationwide is foundational to democracy, it has proven to be quite the operational challenge. In 2022, The U.S. employed over 5,000 people dedicated to managing, and processing FOIA requests. Between labor and technology, costs for FOIA processing alone ran upwards of $580 Million dollars in 2022, not including Privacy Act requests.
The volume of FOIA requests each year continues to grow at a rate of 5 to 10% each year, and the backlog of requests is growing in tandem. A “simple” FOIA request takes agencies an average of 40 days to respond to, up from 30 days in 2020, while “complex” FOIA requests average about a 170-day response time.
Areas for Business Process Improvement
The processing of FOIA requests is nuanced and complex, and one of the major delays results from the time required for agency employees to redact all PII and sensitive information prior to fulfilling the FOIA request. Both over-redaction and under-redaction have potential legal ramifications for government agencies—trapping agency personnel between efficiency and compliance—while the backlog continues to grow.
Agencies need technology that allows them to do more with less in order to reduce backlog and take on the annual growth in requests without increasing headcount.
The Hyperscience Response to Redaction Challenges
Hyperscience offers an intelligent document processing solution that leverages proprietary machine Learning models and natural language processing to identify and redact PII and other sensitive entities within a document.
Out of the box, Hyperscience’s machine learning models can identify these sensitive entities and present them to a FOIA reviewer. FOIA personnel can then quickly review the machine’s suggested redactions, remove any “over-redactions,” and add any additional redactions through a point and click interface. Once the document is redaction-ready, a click of approval from the reviewer automatically creates a redacted copy from the original source document.
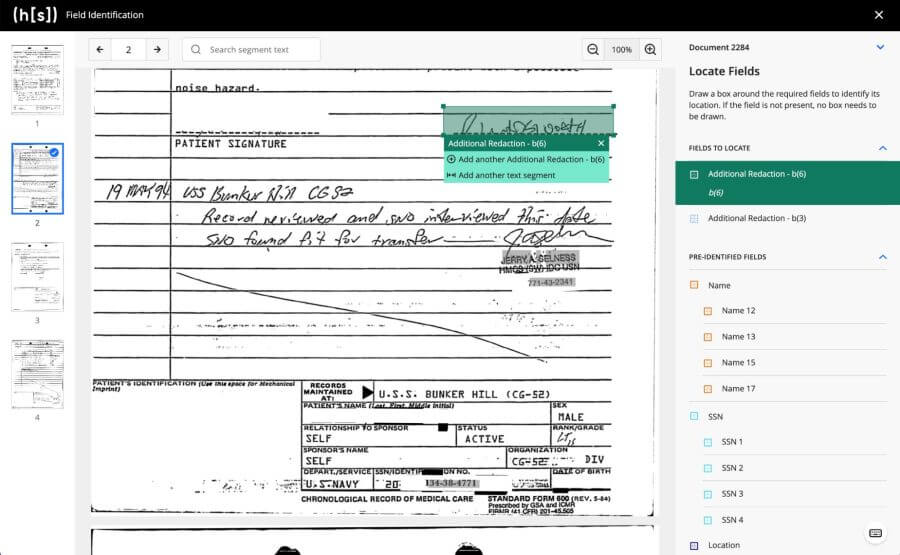
Some cornerstones of Hyperscience’s redaction functionality include:
Automated Redaction Suggestions
Hyperscience’s AI-Assisted Redaction solution identifies names, locations, addresses, phone numbers, emails, dates, and social security numbers out-of-the-box. Additionally, Hyperscience provides the flexibility needed to add further entities to the list.
Intuitive User Interface
After machine processing, Hyperscience presents the suggested redactions to the FOIA reviewer to confirm, add, or remove any redactions necessary.
Immutable Redactions
Hyperscience creates a redacted version of the original document with black boxes covering sensitive entities. The redaction boxes are completely immutable, materially changing the pixels on the document copy so no find or search capabilities will unveil the underlying data.
Exclusion Watermarks
Based on the redacted entity type, Hyperscience assigns exemptions to each redaction, placing the exemption code in white text over the black box redaction. These exemption code assignments are easily configurable to your documents and process.
Deployment and Interoperability
Hyperscience can be deployed on-premise or in a cloud configuration of your choice. Hyperscience comes with REST API capabilities as well as pre-built connectors, allowing for seamless integration to document repositories, FOIA / Privacy Act process management systems, and additional downstream systems and analytics tools.
Proof of Concept Results
After deploying and testing the AI-assisted redaction solution as a proof of concept for a Department of Defense agency, the outcome showed tremendous potential. The POC was designed to test the number of pages processed per hour with Hyperscience in comparison to the existing manual solution, as well as to test machine learning model accuracy. The process involved 3 human data keyers processing 130 live service treatment records, totaling 4,429 pages.
Upon completion, the analysis concluded that human data keyers were 188% more productive with the AI-assisted redaction, processing 575 pages per hour in comparison to the current solution, in which keyers complete just 200 pages per hour. The machine learning model properly identified 92% of all PII entities that should be redacted, which allowed the human data keyers to focus their attention on much fewer fields, and save time in review / manual redaction.
Simplifying Redaction at Scale with AI-Assisted Solutions
At scale, Hyperscience has proven to dramatically reduce the manual effort required to redact PII from documents, regardless of if they are being requested for FOIA, Privacy Act, or other regulatory requirements. Hyperscience’s AI-Assisted Redaction solution streamlines the redaction process for human reviewers, allowing them to review more pages per hour, and lower the chance for missed redactions.
To learn more about Hyperscience’s redaction capabilities, dive deeper into the functionality here, where we’ve outlined additional applications for AI-assisted redaction. Don’t miss the demo video that highlights how the Hyperscience platform redacts sensitive information with ease and accuracy, and as always, drop us a line if you have any questions.

